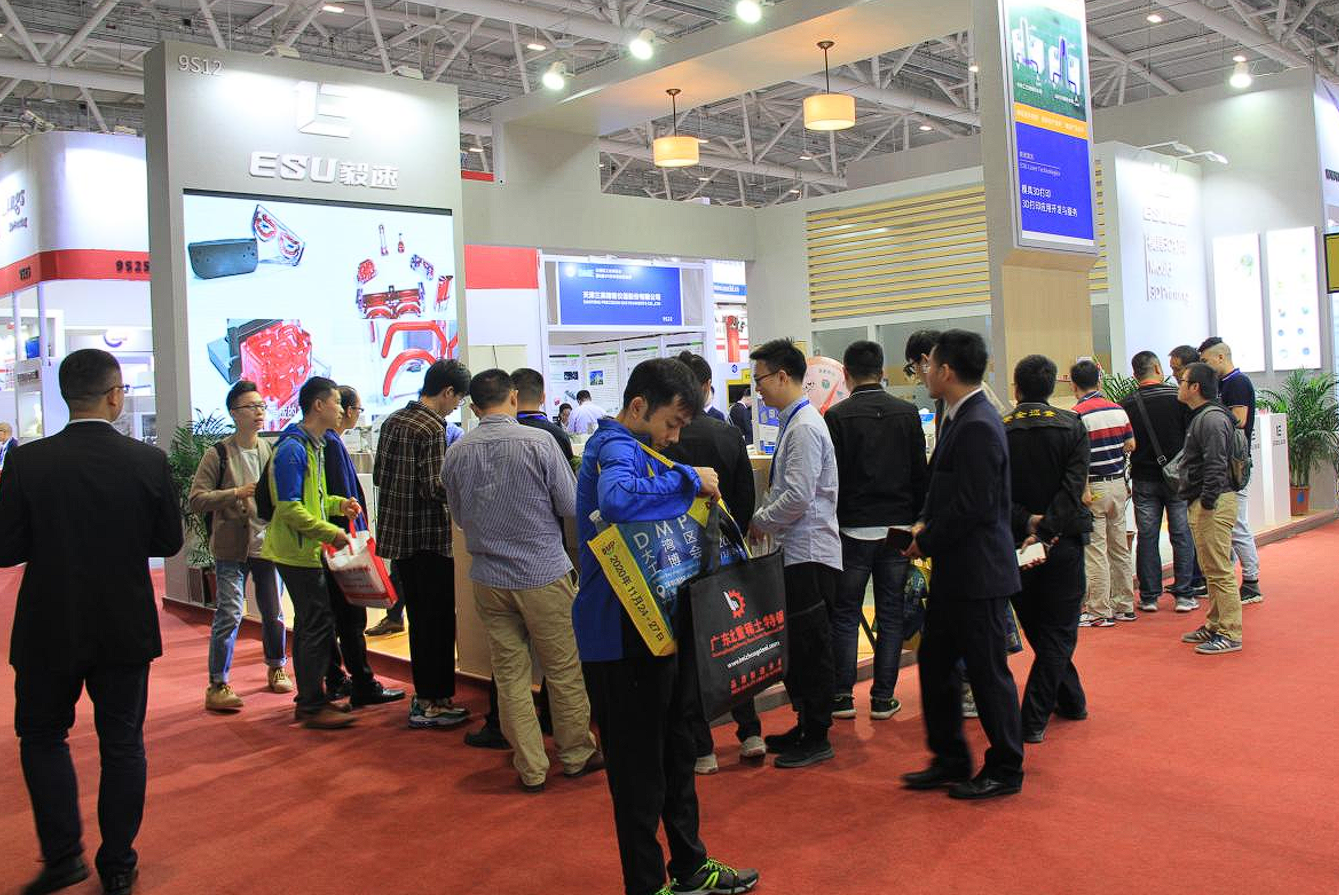
Over the past decade or so since the application of 3D printing in mold making, participants in the industrial chain have either only sold printing equipment or only engaged in traditional mold processing. This has led to a situation where "downstream users cannot make full use of the technology, and upstream suppliers cannot fully understand the demands." Technology and industry cannot be deeply integrated, and the value of 3D-printed molds cannot be fully released.
However, in China, there is a company whose core team has deep roots in traditional mold manufacturing but quickly embraced the rise of 3D printing technology. Over the years, it has always focused on the segmented applications of molds. Today, it has served more than 3,000 customers, accumulated more than 200,000 application cases, and is favored by many Fortune 500 companies. It is ESU 3D Printing, an enterprise that defines itself as "the one that understands molds better in the 3D printing field and understands 3D printing better in the mold field!"

For many years, Isu Laser has been working to bridge the gap between these two fields. The biggest challenge in achieving this "dual understanding" is not the technology itself, but a deep understanding of both the technology and the products.
"More Knowledgeable About Molds in the 3D Printing Field"
ESU 3D Printing has been researching the application of 3D printing technology in the mold field since 2018, and its core team all have more than 20 years of experience in mold manufacturing. The deep cultivation in the mold field enables it to deeply understand the usage scenarios and actual needs of mold applications. This understanding is not superficial but goes deep into every detail of mold manufacturing.

For example, ESU 3D Printing understands what kind of materials the mold industry needs and whether the existing materials for 3D printing can meet those needs; what levels of polishing requirements the surface quality of the final mold products must achieve and the level of 3D printed products in this regard; whether 3D printing can optimize specific problems faced by molds in application, such as gas trapping and cracking, and many other practical issues encountered by users.
Therefore, only by truly understanding these characteristics in mold applications can we targeted solve a series of problems in various links of 3D printing. It is difficult to accurately solve problems by using generalized materials and processes.
"More Knowledgeable About 3D Printing in the Mold Field"
However, merely understanding mold applications is insufficient; without expertise in 3D printing, it remains difficult to produce high-quality molds. Even today, there are still some mold enterprises that have purchased 3D printers but can't use them well. Instead, they entrust ESU 3D Printing to develop products for them. The key reason is that they haven't fully understood the manufacturing characteristics of 3D printing technology.
This is largely because what the upstream supply chain provides are generalized products, including materials, processes, and even services, which cannot fully meet the needs of mold applications. For example, how can 3D printing equipment providers help mold users achieve better exhaust through design or processes? How can material suppliers understand the specific usage needs of the mold industry to develop more suitable special materials for mold applications? At this time, it is necessary to understand both molds and 3D printing.

Based on its understanding of mold application scenarios and years of usage experience, ESU 3D Printing has not only developed metal 3D printing equipment but also researched and developed special 3D printing materials, special processes, and engineering experience for molds. It has transformed the manufacturing potential of 3D printing technology into visible and usable productivity improvements in the mold industry.

Mold 3D Printing Integrated Solutions
Dedicated to Empowering Users to Fully Leverage the Technology
In response to the upgrading and transformation needs of traditional mold manufacturing enterprises, ESU 3D Printing has launched an overall 3D printing solution for molds. What it provides is not just superficial products such as equipment, materials, and process packages, nor is it merely teaching users which materials to use and how to operate the printer. It also includes aspects such as how to conduct product design based on the manufacturing characteristics of 3D printing, what finishing and post-processing issues need to be addressed after manufacturing, and almost all other possible concerns. Its goal is to help users integrate 3D printing into their manufacturing systems without any worries.
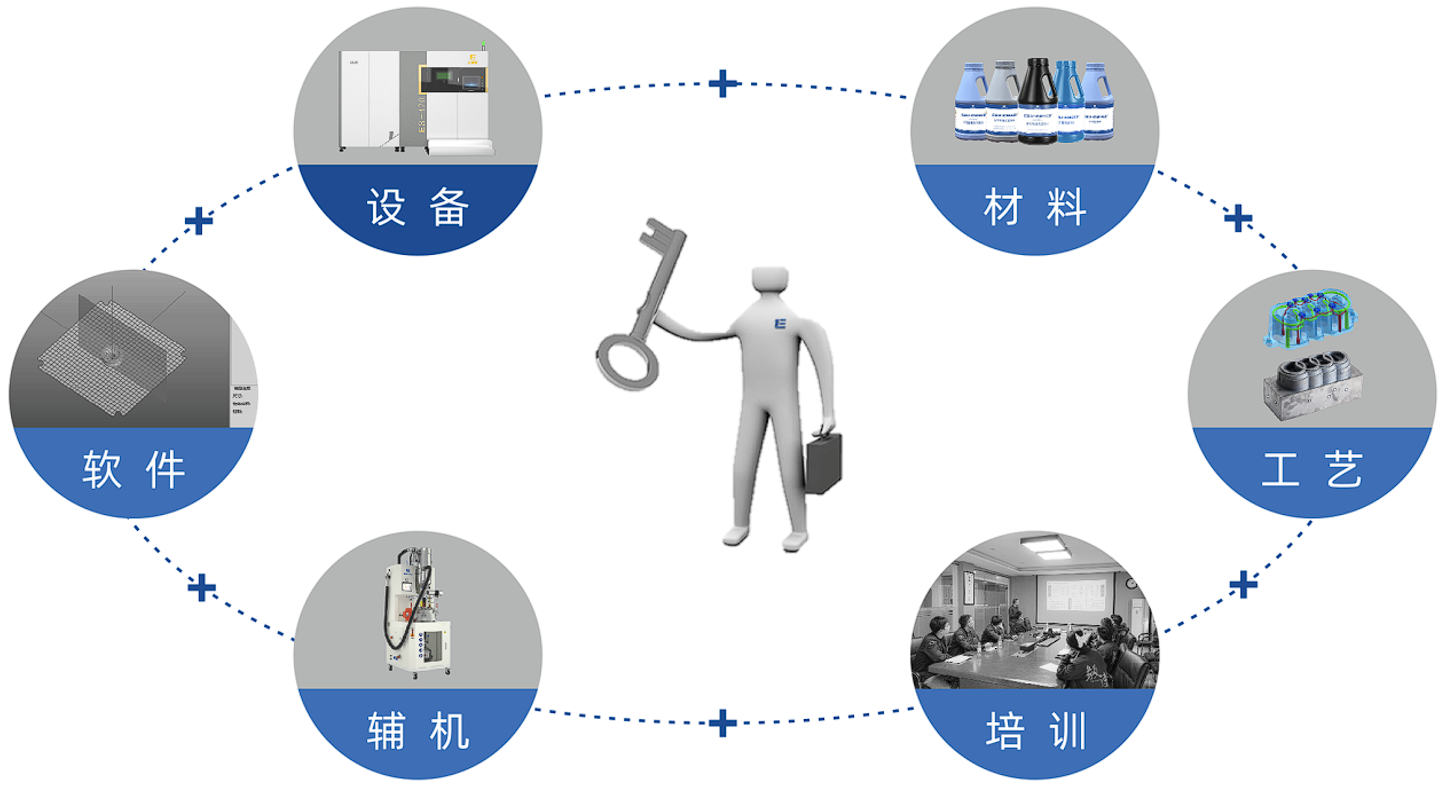
➡️ In terms of equipment, ESU 3D Printing's metal 3D printers have been iterated to the third-generation products. Their mainstream forming size and flexible multi-laser configuration can fully meet the core needs of the mold industry for printing size, forming efficiency, and manufacturing costs.
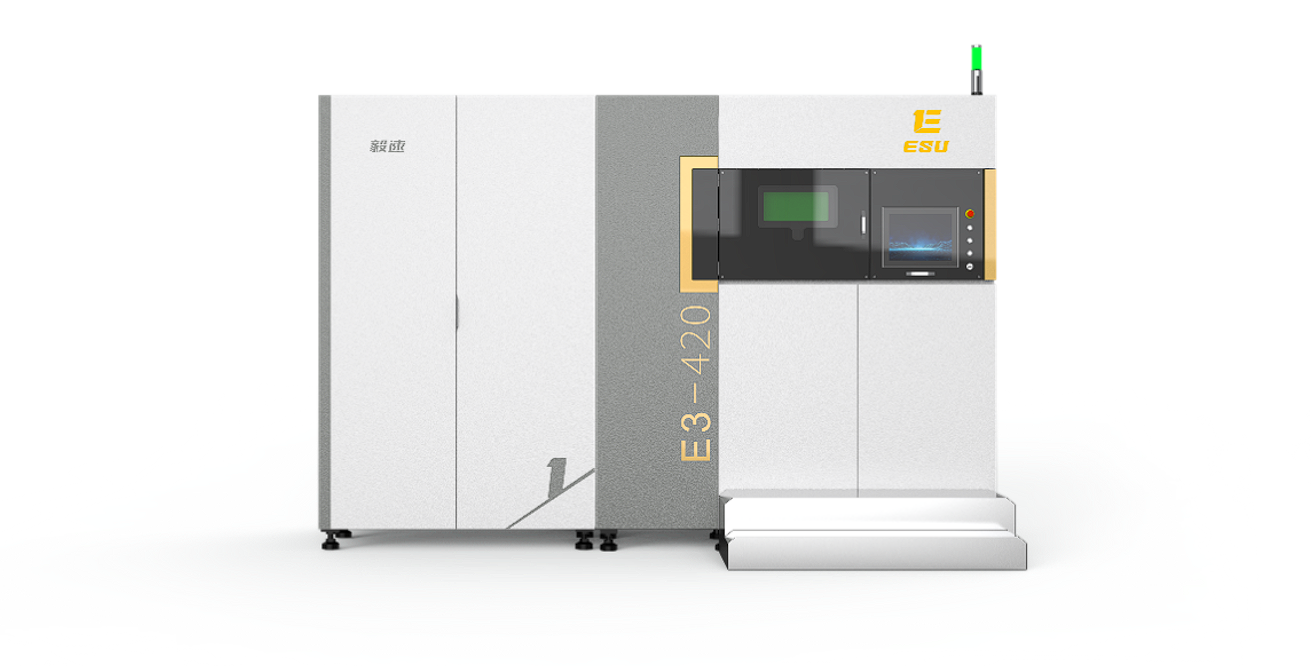

➡️ In terms of craftsmanship, ESU not only provides general 3D printing process packages, but also has developed special printing processes for specific features based on the characteristics of molds, including conformal cooling channel technology, porous steel technology, grafting printing technology, non-subtractive printing technology, and product post-processing technology. The development of these specific processes demonstrates the importance of cross-integration in improving product performance.

➡️In terms of materials, ESU 3D Printing has a deep understanding of the pain points and needs in mold applications. It has collaborated with the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Shanghai Jiao Tong University to jointly develop a series of 3D printing materials specifically for molds, which are respectively suitable for requirements such as high polishing, high wear resistance, and high thermal conductivity. Compared with general-purpose material brands, these materials have stronger application targeting.

➡️In terms of engineer training, apart from the necessary training on the operation methods of 3D printers, the most important service lies in how to design molds based on 3D printing technology and how to understand the impact of the technology on products. This service cannot be provided by other enterprises engaged in non-mold industry applications, including how to determine the cooling and ventilation positions of mold parts, how to ensure the ventilation function, and how to distinguish the contour changes of mold waterways during the printing process, etc.
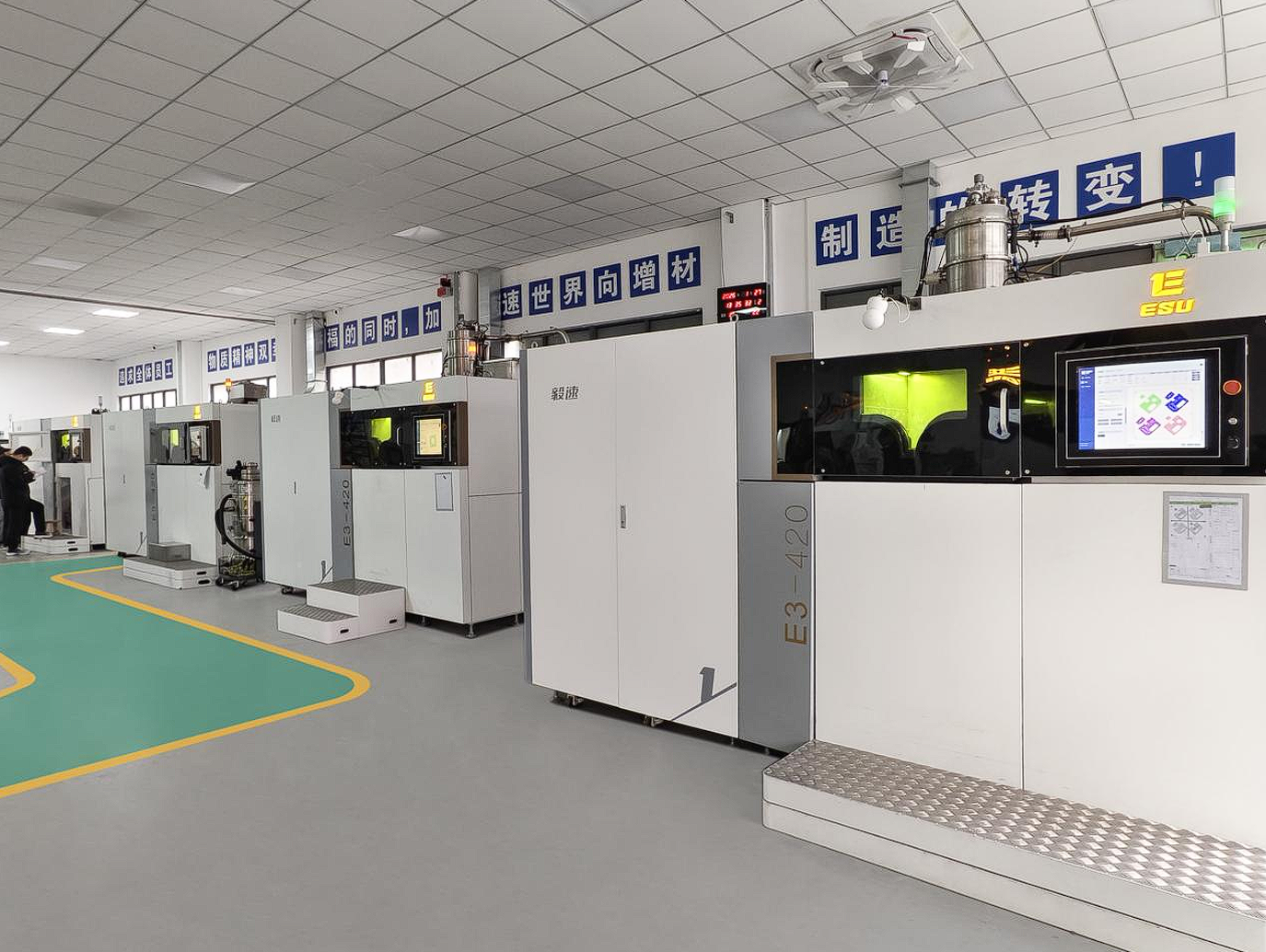

In addition, ESU 3D Printing also conducts feasibility analysis of integrated solutions for users. In addition to the above-mentioned services, it also includes production site planning, etc., to help users choose the most suitable solution.
Dual Identities, Single Mission
